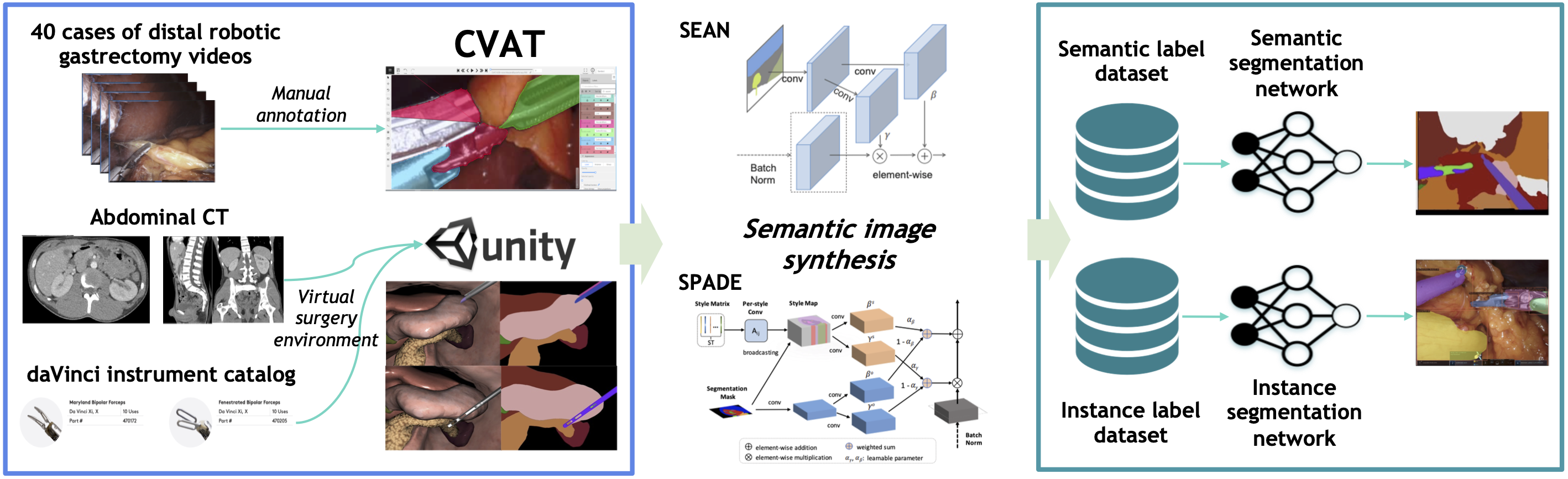
Experiments
We investigated the impact of synthetic training data on instance and semantic segmentation performance.
Specifically, we evaluated two categories of synthetic data—manually synthesized (MS) and
domain-randomized synthetic (DRS)—using three semantic synthesis models:
SPADE, SEAN, and SRC. In contrast to our previous work, we
additionally explored the efficacy of the SRC model in performing unsupervised image-to-image
translation to generate photo-realistic synthetic training images.
Implementation Details
We utilized MMDetection v3.2.0 [Chen et al., 2019b] and MMSegmentation v1.2.2 [MMSegmentation Contributors,
2020], built upon MMCV v1.2.0, MMEngine v0.10.3, PyTorch v2.1.2, and TorchVision v0.16.2, representing the
latest available versions at the time of writing. For image synthesis, software versions were consistent with
those in prior studies. Notably, updates to these major packages introduced deviations from previous findings
[Yoon et al., 2022]. To ensure reproducibility and mitigate randomness-induced variability, a fixed random seed
was used throughout all training and evaluation procedures.
All segmentation models incorporating real and synthetic data were trained for 40 epochs. For fairness, training
epochs for models utilizing only real data were adjusted to match the total number of iterations experienced by
models trained with combined real and synthetic data. The best-performing checkpoint was selected as the
representative model from each training run. Synthetic data-trained models typically reached optimal performance
around epoch 34, confirming no additional performance gains beyond 40 epochs. Detailed hyperparameters are
provided in Table 12.
Manual synthetic (MS) data generation initially produced 3400 images. Subsequently, images containing objects
(instrument head or entire instrument) below a pixel threshold of 10,900 were excluded. Applying Object
Size-aware Random Crop (OSRC), we generated the MS+C dataset. OSRC utilized a fixed random seed (0) and targeted
object size ratios within the median to 75th percentile range of real object distributions, determined
empirically. Further refinement by reassigning the background class to "other anatomical tissues" resulted in
the MS+C+B dataset. Each MS dataset variant was photo-realistically synthesized using SPADE, SEAN, and SRC
models, denoted as ModelName(MS+...). These synthesized datasets were combined with real training data (R) as
R+ModelName(MS+...) for subsequent training.
Domain-randomized synthetic (DRS) data production generated 4474 images. Initially applying OSRC, we then
eliminated images containing objects with a size ratio below 0.0005. Using identical random seed and size
distribution parameters as in MS data, the refined DRS data served as sources for copy-paste augmentation. To
streamline the process, augmentation via copy-paste and subsequent photo-realistic synthesis were performed
offline, with augmented images and masks stored before training. Half of the training dataset comprised
augmented copy-paste (CP) data combined from real and DRS masks, and half consisted of original real data,
denoted as R+ModelName(R+DRS+...+CP). For comparative analysis, we also generated a baseline dataset synthesized
exclusively from real masks, labeled as R+ModelName(R+CP). Detailed statistics of domain-randomized data
utilized in copy-paste augmentation are summarized in Table 11.
Relative Performance Improvement
To quantitatively measure the benefit provided by synthetic data relative to real data, we propose a metric
termed Relative Performance Improvement. Specifically, the Relative performance improvement
metric is defined as:
Relative Metric = (MetricR+Syn - MetricR) / MetricR
where the metric can be AP, IoU, or Accuracy. By calculating this ratio, we explicitly assess the relative
performance gains attributable to synthetic data augmentation, denoted as Relative AP,
Relative IoU, and Relative Acc.
Instance Segmentation with Manual Synthetic
Data
To quantitatively evaluate segmentation performance, we employed two state-of-the-art segmentation models,
Cascade Mask R-CNN (CMR) and Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC), and assessed their
bounding box and mask performance using mean average precision (box mAP and mask
mAP) as defined by the MS-COCO benchmark [Lin et al., 2014]. Additionally, we calculated mean
Relative Average Precision (box mRAP and mask mRAP) to explicitly measure the
relative performance enhancement achieved by synthetic data augmentation compared to real data alone.
As summarized in Table 2, incorporating synthetic data consistently improved the mean box AP across both CMR and
HTC models. However, mask AP improvement was less consistent. Notably, the best overall performances were
achieved using the R+SPADE(MS+C+B) dataset, yielding the highest mean box AP of
54.92 and mask AP of 50.04 for CMR.
A detailed class-specific analysis in Table 3 highlights results that differ substantially from the aggregate
performance. Specifically, Table 3 presents the top 10 and bottom 10 classes based on performance improvements
for instrument detection using the CMR model trained on the R+SPADE(MS+C+B) dataset. This
reveals significant class-specific variations, emphasizing the necessity of detailed, class-level analysis
beyond aggregated metrics.
Table 2. Performance metrics (mean mAP ± standard deviation) for Cascade Mask R-CNN
(CMR) and Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) trained on manual synthetic (MS) datasets.
Best performance for each model is indicated in bold.
| Model |
Dataset |
Box mAP (Mean ± Std.) |
Mask mAP (Mean ± Std.) |
| Cascade Mask R-CNN (CMR) |
R |
53.93 ± 0.98 |
49.75 ± 1.05 |
| R+SEAN(MS) |
54.32 ± 1.25 |
49.00 ± 1.22 |
| R+SPADE(MS) |
54.31 ± 1.43 |
48.98 ± 1.41 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C) |
54.69 ± 1.19 |
49.46 ± 1.23 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C) |
54.82 ± 1.38 |
49.58 ± 1.46 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
54.89 ± 0.97 |
49.55 ± 1.10 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
54.92 ± 1.04 |
50.04 ± 1.07 |
| Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) |
R |
55.06 ± 0.86 |
51.67 ± 0.56 |
| R+SEAN(MS) |
55.55 ± 1.34 |
50.95 ± 1.08 |
| R+SPADE(MS) |
55.51 ± 0.77 |
50.88 ± 1.05 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C) |
56.09 ± 0.78 |
51.44 ± 0.97 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C) |
56.23 ± 1.08 |
51.40 ± 1.22 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
56.20 ± 0.93 |
51.37 ± 1.13 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
56.36 ± 0.94 |
51.77 ± 1.04 |
Table 3. Relative performance improvements (%) of Cascade Mask R-CNN using synthetic data
(R+SPADE(MS+C+B)) compared to real data alone across three cross-validation sets. The top 10
classes with the greatest improvement and the bottom 10 classes with the least improvement are shown.
| Category (Top 10) |
Real Box mAP |
Relative Box mAP |
Real Mask mAP |
Relative Mask mAP |
| DT |
20.90 |
+23.29 |
27.20 |
+5.88 |
| ND |
31.10 |
+18.11 |
6.93 |
-0.96 |
| Liver |
32.33 |
+15.15 |
39.07 |
+7.08 |
| CAG_H |
14.07 |
+11.37 |
10.47 |
+8.92 |
| SB |
41.70 |
+10.23 |
38.73 |
+4.13 |
| GZ |
34.00 |
+8.43 |
46.10 |
+1.81 |
| Spleen |
26.13 |
+7.78 |
30.63 |
+5.88 |
| Pancreas |
27.30 |
+7.69 |
27.60 |
+11.71 |
| Stomach |
41.83 |
+7.09 |
47.40 |
+4.57 |
| S_H |
57.17 |
+6.88 |
53.00 |
+1.51 |
| Category (Bottom 10) |
Real Box mAP |
Relative Box mAP |
Real Mask mAP |
Relative Mask mAP |
| SCA_W |
83.07 |
-0.48 |
83.10 |
-0.84 |
| HA_B |
70.43 |
-0.62 |
64.97 |
-1.03 |
| CF_W |
65.47 |
-0.81 |
58.27 |
+0.11 |
| MLCA_B |
69.33 |
-1.49 |
67.90 |
-2.16 |
| S_B |
42.07 |
-1.66 |
39.63 |
+3.36 |
| SCA_B |
82.10 |
-1.66 |
77.07 |
+0.74 |
| HA_H |
53.80 |
-1.80 |
32.43 |
-3.08 |
| SI |
73.47 |
-2.27 |
71.30 |
-3.04 |
| MLCA_W |
76.40 |
-2.79 |
68.30 |
-0.29 |
| MLCA_H |
68.20 |
-4.30 |
55.77 |
-2.51 |
Semantic Segmentation with Manual Synthetic
Data
We evaluated semantic segmentation performance using two representative models, DeepLabV3+ and
UperNet, employing standard metrics including mean Intersection-over-Union
(mIoU) and mean Accuracy (mAcc). Additionally, we introduced mean
Relative IoU (mRIoU) and mean Relative Accuracy (mRAcc) metrics, analogous to those
used in our instance segmentation evaluation, to quantitatively assess improvements from synthetic data
augmentation.
Table 4 summarizes semantic segmentation results across synthetic datasets. Interestingly, uncropped synthetic
datasets generally outperformed cropped variants, contrasting the instance segmentation findings. Among
synthetic data combinations, R+SPADE(MS+C+B) achieved the highest performance for both
segmentation models. We attribute the observed lower relative improvements compared to instance segmentation to
the already high baseline performance obtained with the real dataset alone (e.g., 74.63 Mean mIoU with UperNet).
A more detailed analysis of class-level performances (Table 5) for semantic segmentation using UperNet trained
on R+SPADE(MS+C+B) highlights notably smaller relative gains compared to instance segmentation.
This is primarily due to the already high baseline accuracy for the top-performing classes. Furthermore, unlike
instance segmentation, all uncropped synthetic datasets consistently outperformed cropped ones, indicating
task-dependent sensitivity to cropping strategies.
Table 4. Performance metrics (Mean ± Std.) for UperNet (UPN) and
DeepLabV3+ (DLV3+) trained on manual synthetic (MS) datasets across three cross-validation
datasets. Best performance for each model is indicated in bold.
| Model |
Dataset |
Mean mIoU (± Std.) |
Mean mAcc (± Std.) |
| UperNet (UPN) |
R |
74.63 ± 1.04 |
83.35 ± 0.86 |
| R+SEAN(MS) |
72.87 ± 0.77 |
82.10 ± 0.87 |
| R+SPADE(MS) |
73.42 ± 0.90 |
82.60 ± 0.72 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C) |
72.74 ± 0.97 |
82.05 ± 0.69 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C) |
73.16 ± 1.32 |
82.49 ± 1.10 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
72.44 ± 0.90 |
81.93 ± 0.65 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
72.60 ± 1.25 |
81.99 ± 0.89 |
| DeepLabV3+ (DLV3+) |
R |
74.62 ± 0.84 |
83.65 ± 0.74 |
| R+SEAN(MS) |
72.71 ± 0.90 |
82.10 ± 0.65 |
| R+SPADE(MS) |
73.18 ± 0.97 |
82.53 ± 0.93 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C) |
72.04 ± 1.31 |
81.84 ± 1.26 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C) |
72.56 ± 1.30 |
82.14 ± 1.10 |
| R+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
71.70 ± 0.78 |
81.62 ± 0.87 |
| R+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
72.07 ± 0.86 |
81.81 ± 0.94 |
Table 5. Relative performance improvements (%) for UperNet trained on
R+SPADE(MS) compared to the R dataset across three cross-validation datasets. The top 10 and
bottom 10 classes based on mean IoU (mIoU) are listed.
| Category (Top 10) |
Real Mean mIoU |
Relative Mean mIoU (%) |
Real Mean mAcc |
Relative Mean mAcc (%) |
| Spleen |
31.23 |
+3.10 |
35.65 |
+3.73 |
| Pancreas |
56.54 |
+1.73 |
69.04 |
+1.50 |
| Gallbladder |
59.93 |
+0.91 |
66.01 |
+2.06 |
| Stomach |
67.03 |
+0.26 |
84.97 |
+0.36 |
| SCA_B |
80.75 |
+0.14 |
86.37 |
+0.34 |
| TO_T |
82.85 |
-0.06 |
92.26 |
-0.42 |
| GZ |
92.96 |
-0.20 |
96.41 |
0.00 |
| ET |
91.69 |
-0.27 |
97.69 |
-0.13 |
| Liver |
78.33 |
-0.28 |
87.50 |
+0.38 |
| SCA_W |
88.27 |
-0.42 |
93.49 |
-0.07 |
| Category (Bottom 10) |
Real Mean mIoU |
Relative Mean mIoU (%) |
Real Mean mAcc |
Relative Mean mAcc (%) |
| MBF_B |
73.83 |
-2.46 |
84.21 |
-2.49 |
| SCA_H |
84.40 |
-2.79 |
84.42 |
-2.27 |
| S_H |
81.78 |
-2.93 |
89.56 |
-0.35 |
| SI |
75.20 |
-3.08 |
81.52 |
-2.51 |
| ND |
57.32 |
-3.39 |
69.86 |
-2.54 |
| CF_W |
76.53 |
-3.60 |
87.67 |
-2.60 |
| MLCA_H |
79.54 |
-4.08 |
89.39 |
-1.72 |
| HA_H |
65.67 |
-4.33 |
78.38 |
-2.60 |
| S_B |
78.43 |
-4.93 |
85.67 |
-3.47 |
| CAG_H |
41.10 |
-7.40 |
52.22 |
-3.04 |
Domain Randomized Synthetic Data
Tables 6 and 7 summarize results obtained using domain-randomized synthetic (DRS) data as a
source for copy-paste (CP) augmentation across segmentation models. Our results demonstrate that DRS-based
copy-paste consistently improves performance for instance segmentation models, as evidenced by increased box and
mask AP scores. However, when extending this augmentation method to semantic segmentation, no performance gains
were observed. We hypothesize that the lack of improvement in semantic segmentation models is primarily due to
their already strong baseline performance with real data, limiting the potential effectiveness of the additional
synthetic augmentation.
Table 6. Performance metrics (Mean ± Std.) of Cascade Mask R-CNN (CMR) and
Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) trained using domain-randomized synthetic (DRS) datasets combined
with the copy-paste (CP) augmentation strategy across three cross-validation datasets. Best results are
highlighted in bold.
| Model |
Dataset |
Box Mean mAP (± Std.) |
Mask Mean mAP (± Std.) |
| Cascade Mask R-CNN (CMR) |
R+SPADE(R+CP) |
58.09 ± 0.91 |
50.86 ± 1.06 |
|
R+SPADE(R+DRS+C+B+CP) |
58.18 ± 0.67 |
51.10 ± 0.97 |
| Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) |
R+SPADE(R+CP) |
59.68 ± 0.65 |
52.96 ± 0.89 |
|
R+SPADE(R+DRS+C+B+CP) |
59.68 ± 0.75 |
52.95 ± 0.96 |
Table 7. Performance metrics (mean ± std.) for UperNet (UPN) and
DeepLabV3+ (DLV3+) models using copy-paste augmentation with Domain Randomized Synthetic
(DRS) dataset. Metrics are averaged over three cross-validation datasets. Best results are highlighted in
bold.
| Model |
Dataset |
Mean mIoU (± Std.) |
Mean mAcc (± Std.) |
| UperNet (UPN) |
R+SPADE(R+CP) |
70.26 ± 1.08 |
80.17 ± 0.78 |
|
R+SPADE(R+DRS+C+B+CP) |
70.08 ± 0.99 |
80.02 ± 0.74 |
| DeepLabV3+ (DLV3+) |
R+SPADE(R+CP) |
72.39 ± 4.05 |
82.31 ± 3.15 |
|
R+SPADE(R+DRS+C+B+CP) |
69.46 ± 1.02 |
79.88 ± 0.85 |
Real Data Size vs. Synthetic Data
Effectiveness
Tables 8 and 9 present segmentation results obtained using a reduced-size real dataset (R1(H),
half-sized dataset for cross-validation set 1) combined with a full-scale synthetic dataset. Unlike previous
results shown in Table 2, where the CMR model achieved the best performance using
SPADE(MS+C+B), here the highest improvement in mAP was obtained with
SPADE(MS+C) data. Interestingly, despite a reduced real-data baseline, semantic segmentation
models (UperNet and DeepLabV3+) maintained robust performance (~71 mIoU) even
without synthetic augmentation, and thus no overall improvements were observed when incorporating synthetic
data. This indicates semantic segmentation models are less sensitive to synthetic data augmentation in scenarios
with moderately reduced training data. Future work will further investigate scenarios with significantly smaller
real training datasets.
Table 8. Performance metrics (box mAP and mask mAP) for Cascade Mask R-CNN
(CMR) and Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) trained on Manual Synthetic (MS) datasets
combined with half-sized real data (H). The highest performance per model is highlighted in bold.
| Model |
Dataset |
Box mAP |
Mask mAP |
| Cascade Mask R-CNN (CMR) |
R1(H) |
49.14 |
44.38 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS) |
49.36 |
43.19 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS) |
50.74 |
44.04 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C) |
50.51 |
44.45 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C) |
51.40 |
44.93 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
50.78 |
44.61 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
51.35 |
44.86 |
| Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) |
R1(H) |
51.02 |
45.38 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS) |
51.40 |
45.93 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS) |
51.31 |
45.65 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C) |
51.96 |
46.44 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C) |
52.39 |
46.71 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
52.65 |
46.90 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
52.76 |
46.73 |
Table 9. Performance metrics (mIoU and mAcc) for UperNet (UPN) and
DeepLabV3+ (DLV3+) trained on manual synthetic (MS) datasets combined with half-sized real
data (H). Metrics are averaged over three cross-validation datasets. The highest performance per model is
highlighted in bold.
| Model |
Dataset |
mIoU (%) |
mAcc (%) |
| UperNet (UPN) |
R1(H) |
71.74 |
80.97 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS) |
69.03 |
79.04 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS) |
68.60 |
78.78 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C) |
66.95 |
77.34 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C) |
68.38 |
78.32 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
65.58 |
76.25 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
67.31 |
77.39 |
| DeepLabV3+ (DLV3+) |
R1(H) |
71.77 |
81.04 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS) |
68.28 |
78.82 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS) |
68.23 |
78.69 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C) |
65.78 |
76.96 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C) |
67.03 |
77.67 |
| R1(H)+SEAN(MS+C+B) |
65.74 |
76.73 |
| R1(H)+SPADE(MS+C+B) |
66.17 |
77.09 |
Semantic Image Synthesis
We evaluated the effectiveness of synthetic data generated by the SPADE and SEAN models for training both
instance and semantic segmentation networks. To quantitatively assess image synthesis quality, we adopted the
three-step evaluation framework proposed by Park et al. 2019 and Zhu et al., 2020: (1) segmentation models were
trained solely on real data; (2) segmentation models were evaluated on both real validation data and
corresponding synthesized validation sets produced by SPADE and SEAN; (3) the segmentation performance on
original and synthesized validation sets was directly compared.
Table 10 presents the evaluation results on photo-realistic synthesized validation sets as well as the average
mAP achieved when training segmentation models with synthetic datasets from each synthesis method. While both
SPADE and SEAN produced high-quality photo-realistic data, SEAN achieved superior validation set fidelity across
most metrics. However, in terms of overall synthetic training data effectiveness (average mAP), SPADE-generated
datasets provided comparable or slightly higher improvements, suggesting a task-dependent distinction between
visual realism and segmentation model performance.
Table 10. Performance metrics for evaluating the photo-realistic synthesis abilities of
SPADE and SEAN models. "AVG Syn" indicates the average segmentation model
performance trained with SPADE/SEAN-generated synthetic datasets (MS/F/C/B) evaluated on the R1-valid dataset.
| Model |
Train/Valid |
mAP/mIoU |
mAP/mAcc |
AVG Syn mAP/mIoU |
AVG Syn mAP/mAcc |
| Cascade Mask R-CNN (CMR) |
R1/R1-valid |
0.543 |
0.497 |
– |
– |
| R1/SEAN(R1-valid) |
0.472 |
0.437 |
55.25 |
49.33 |
| R1/SPADE(R1-valid) |
0.411 |
0.373 |
55.00 |
49.43 |
| Hybrid Task Cascade Mask R-CNN (HTC) |
R1/R1-valid |
0.555 |
0.516 |
– |
– |
| R1/SEAN(R1-valid) |
0.486 |
0.453 |
56.38 |
51.10 |
| R1/SPADE(R1-valid) |
0.431 |
0.398 |
56.15 |
51.05 |
| UperNet (UPN) |
R1/R1-valid |
73.73 |
87.87 |
– |
– |
| R1/SEAN(R1-valid) |
60.35 |
83.69 |
71.87 |
81.29 |
| R1/SPADE(R1-valid) |
58.30 |
83.92 |
72.47 |
81.85 |
| DeepLabv3+ (DLV3+) |
R1/R1-valid |
88.10 |
74.05 |
– |
– |
| R1/SEAN(R1-valid) |
62.77 |
73.73 |
71.67 |
81.28 |
| R1/SPADE(R1-valid) |
60.73 |
71.54 |
71.98 |
81.33 |
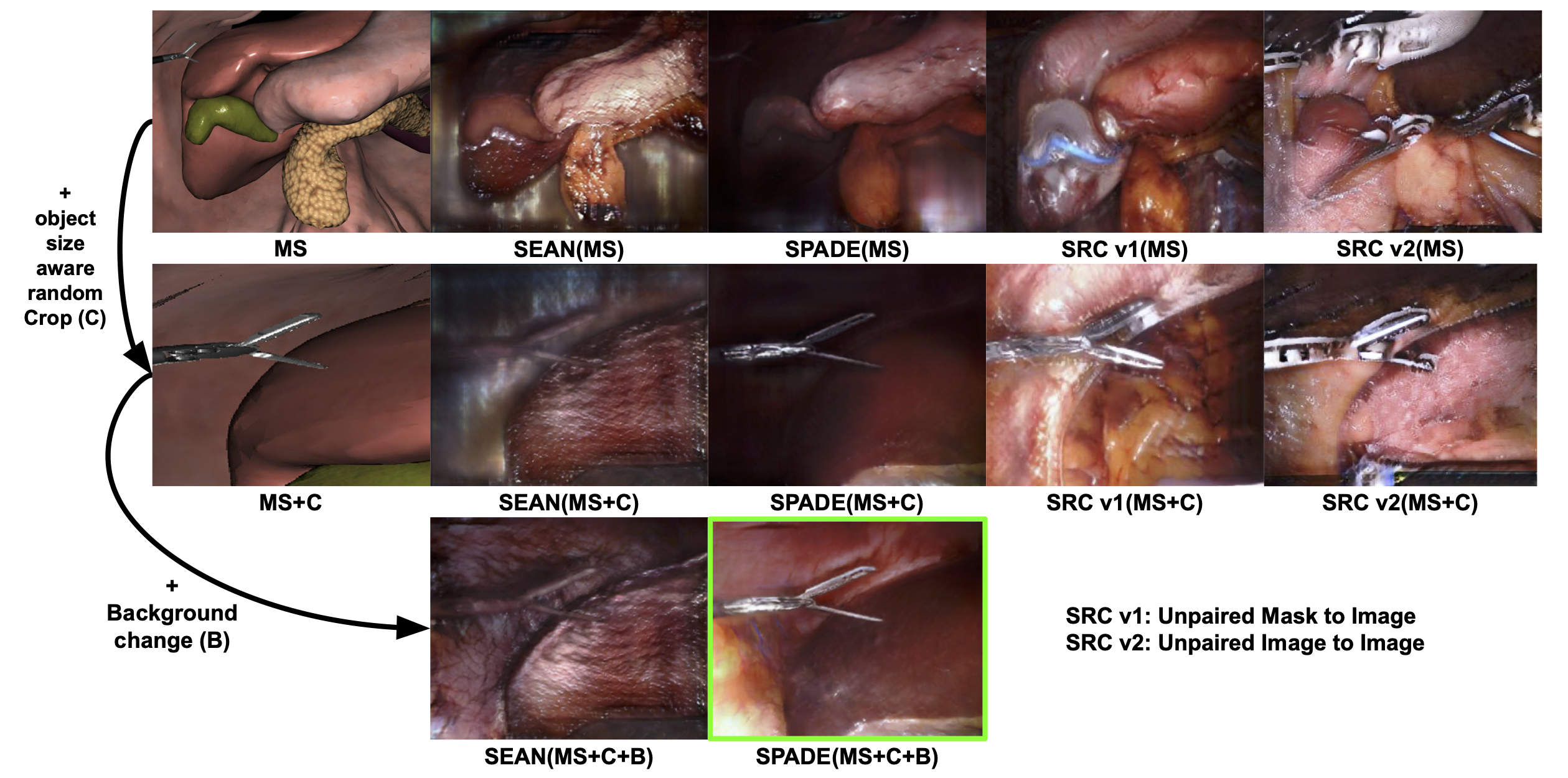
Qualitative Analysis of Synthetic Data
Figure 2 qualitatively illustrates improvements toward photo-realistic synthesis by
sequentially applying Object Size-aware Random Crop (OSRC) and Background Label Enhancement. The initial
synthetic images (first row) differ considerably from real surgical scenes, complicating realistic image
generation. Applying OSRC (second row) effectively aligns object sizes with real distributions, yet unnatural
background textures remain. Subsequently, introducing Background Label Enhancement (third row) significantly
removes these unnatural artifacts, resulting in images closely resembling actual surgical scenes. Notably,
although SEAN exhibits the best quantitative performance with real validation masks (Table 11), this may
indicate model sensitivity or potential overfitting to real data distributions.
Unsupervised Image Translation
We compared the effectiveness of unsupervised image translation (SRC) and supervised semantic image synthesis
methods (SPADE and SEAN) for generating photo-realistic synthetic data, as illustrated in Figure 2. Two SRC
variants were explored: one trained to translate real segmentation masks into real images (analogous to
supervised synthesis methods), and the other directly translating synthetic masks to realistic images.
Qualitative results revealed that both SRC models failed to adequately capture semantic consistency, producing
unnatural synthesis outcomes. We hypothesize that the substantial domain gap between synthetic and real data
prevents the SRC models from accurately learning semantic relationships, resulting in inferior synthesis
quality. Despite its advantage of not requiring labeled pairs, SRC's effectiveness may be significantly limited
when the domain discrepancy is large, highlighting challenges for unsupervised translation in this setting.
Table 11. Class distribution and number of frames per dataset. Each cross-validation set
includes Real# and Test#. Manual synthetic data (MS) and domain randomized synthetic data (DRS) are identical
across all cross-validation sets. (HA: Harmonic Ace, CF: Cadiere Forceps, MBF: Maryland Bipolar Forceps,
MCA: Medium-large Clip Applier, SCA: Small Clip Applier, CAG: Curved Atraumatic Grasper, DT: Drain Tube, OI:
other instruments, OT: other tissues, H: head, W: wrist, B: body)
| Category |
R1 |
R1-valid |
R2 |
R2-valid |
R3 |
R3-valid |
MS |
MS+F |
MS+F+C(B) |
DRS+F+C |
| HA H |
1317 |
450 |
1304 |
463 |
1305 |
462 |
289 |
284 |
523 |
262 |
| HA B |
1268 |
448 |
1285 |
431 |
1272 |
444 |
297 |
286 |
528 |
261 |
| MBF H |
1460 |
486 |
1451 |
495 |
1439 |
507 |
297 |
292 |
582 |
425 |
| MBF W |
1092 |
376 |
1132 |
336 |
1060 |
408 |
286 |
285 |
1705 |
425 |
| MBF B |
672 |
256 |
724 |
204 |
679 |
249 |
273 |
273 |
514 |
402 |
| CF H |
1093 |
338 |
1058 |
373 |
1045 |
386 |
515 |
490 |
611 |
110 |
| CF W |
900 |
258 |
842 |
316 |
856 |
302 |
441 |
425 |
831 |
108 |
| CF B |
854 |
271 |
816 |
309 |
831 |
294 |
407 |
396 |
498 |
103 |
| CAG H |
704 |
231 |
687 |
248 |
705 |
230 |
692 |
690 |
2884 |
78 |
| CAG B |
787 |
269 |
779 |
277 |
803 |
253 |
691 |
688 |
1790 |
77 |
| S H |
329 |
111 |
322 |
118 |
335 |
105 |
293 |
292 |
436 |
560 |
| S B |
305 |
98 |
297 |
106 |
301 |
102 |
298 |
292 |
401 |
560 |
| MLCA H |
287 |
95 |
282 |
100 |
291 |
91 |
300 |
297 |
1314 |
387 |
| MLCA W |
230 |
82 |
233 |
79 |
236 |
76 |
299 |
297 |
554 |
386 |
| MLCA B |
140 |
50 |
142 |
48 |
141 |
49 |
287 |
287 |
405 |
370 |
| SCA H |
277 |
85 |
266 |
96 |
276 |
86 |
300 |
299 |
322 |
156 |
| SCA W |
261 |
78 |
247 |
92 |
258 |
81 |
300 |
299 |
505 |
156 |
| SCA B |
183 |
51 |
179 |
55 |
175 |
59 |
299 |
299 |
460 |
138 |
| SI |
286 |
92 |
273 |
105 |
286 |
92 |
298 |
297 |
297 |
758 |
| ND |
303 |
115 |
322 |
96 |
306 |
112 |
299 |
287 |
999 |
177 |
| DT |
298 |
97 |
296 |
99 |
297 |
98 |
300 |
299 |
301 |
794 |
| SB |
506 |
145 |
484 |
167 |
449 |
202 |
300 |
300 |
729 |
0 |
| DT |
308 |
103 |
284 |
127 |
299 |
112 |
3243 |
3168 |
2250 |
767 |
| Liver |
2785 |
913 |
2745 |
953 |
2741 |
957 |
3399 |
3322 |
3168 |
0 |
| Stomach |
2278 |
776 |
2286 |
768 |
2336 |
718 |
3264 |
3187 |
2603 |
0 |
| Pancreas |
1507 |
574 |
1544 |
537 |
1623 |
458 |
3115 |
3048 |
2131 |
0 |
| Spleen |
338 |
172 |
422 |
88 |
373 |
137 |
2232 |
2163 |
1063 |
0 |
| Gallbladder |
816 |
353 |
935 |
234 |
916 |
253 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| GZ |
2705 |
942 |
2692 |
955 |
2707 |
940 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| TO I |
1569 |
552 |
1571 |
550 |
1654 |
467 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| TO T |
3367 |
1135 |
3352 |
1150 |
3370 |
1132 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Frames |
3375 |
1135 |
3355 |
1155 |
3377 |
1133 |
3400 |
3322 |
3318 |
4474 |
Table 12: Hyper-parameters for Semantic Image Synthesis and Segmentation Models.
(a) Semantic image synthesis: Both SPADE and SEAN employ the hinge loss with identical
hyper-parameter settings (λfeat = 10.0, λkld = 0.005, λvgg = 10.0), and their
generator (G) and
discriminator (D) architectures follow the original implementations. Batch size (BS) and augmentation
strategies are also provided.
(b) Segmentation: Hyper-parameters for DLV3+, UperNet, Cascade Mask R-CNN (CMR), and
Hybrid Task Cascade (HTC) are listed. Here, β denotes momentum, weight decay (WD) and initial learning
rate (LR) are specified along with the LR scheduler (indicating scaling epochs with a factor of 0.1), batch
size (BS), and warmup (WU) parameters. All backbones are pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset.
(a) Hyper-parameters for Semantic Image Synthesis Models
| Method |
D step per G |
Input size |
Optimizer |
Beta |
Init. LR |
Final epoch |
BS |
Augmentation |
| SPADE |
1 |
512x512 |
Adam |
β₁=0.5, β₂=0.999 |
4×10⁻⁴ |
50 |
20 |
resize, crop, flip |
| SEAN |
1 |
512x512 |
Adam |
β₁=0.5, β₂=0.999 |
2×10⁻⁴ |
100 |
8 |
resize, flip |
(b) Hyper-parameters for Segmentation Models
| Method |
Backbone |
Input size |
Optimizer |
Init. LR |
LR scheduler (final) |
BS |
WU (iter) |
WU (ratio) |
| DLV3+ |
ResNet 101 |
512x512 |
SGD |
0.001 |
cos. annealing (300) |
8 |
1000 |
0.1 |
| UperNet |
ResNet 101 |
512x512 |
AdamW |
6×10⁻⁴ |
Poly (300) |
8 |
1500 |
1.0×10⁻⁶ |
| CMR |
ResNet101 |
1333x800 |
SGD |
0.02 |
step [32] (34) |
16 |
1000 |
0.002 |
| HTC |
ResNet101 |
1333x800 |
SGD |
0.02 |
step [32] (34) |
16 |
1000 |
0.002 |